Benin, a small country in West Africa, is steeped in history and culture. It’s the birthplace of Vodun (Voodoo) and home to the ancient Dahomey Kingdom. The country offers a blend of stunning landscapes, from the palm-fringed beaches along its Atlantic coastline to the northern wildlife parks teeming with elephants and lions. The capital, Porto-Novo, and the largest city, Cotonou, offer vibrant markets and colonial architecture. Benin’s rich cultural tapestry, historical significance, and natural beauty make it a unique and intriguing destination.
List of National and Public Holidays in Benin for the year 2025
Here’s the list of holidays in the format you requested:
- New Year’s Day is on 1st January 2025, Wednesday.
- Vaudoun Day is on 10th January 2025, Friday.
- Korité is on 30th March 2025, Sunday.
- Easter Monday is on 21st April 2025, Monday.
- Labour Day is on 1st May 2025, Thursday.
- Ascension Day is on 29th May 2025, Thursday.
- Tabaski is on 6th June 2025, Friday.
- Whit Monday is on 9th June 2025, Monday.
- Independence Day is on 1st August 2025, Friday.
- Assumption Day is on 15th August 2025, Friday.
- Maouloud is on 4th September 2025, Thursday.
- All Saints’ Day is on 1st November 2025, Saturday.
- Christmas Day is on 25th December 2025, Thursday.
List of National and Public Holidays in Benin for the year 2024
- New Year’s Day: Monday, 1 January 2024
- Vaudoun Day: Wednesday, 10 January 2024
- Easter Monday: Monday, 1 April 2024
- Korité (Eid al-Fitr): Wednesday, 10 April 2024
- Labour Day: Wednesday, 1 May 2024
- Ascension Day: Thursday, 9 May 2024
- Whit Monday: Monday, 20 May 2024
- Tabaski (Eid al-Adha): Sunday, 16 June 2024
- Independence Day: Thursday, 1 August 2024
- Assumption Day: Thursday, 15 August 2024
- Maouloud (Prophet Muhammad’s Birthday): Sunday, 15 September 2024
- All Saints’ Day: Friday, 1 November 2024
- Christmas Day: Wednesday, 25 December 2024

Benin, a country rich in history and culture in West Africa, is renowned for its role in the Dahomey Kingdom and as a center of the slave trade. It has a vibrant cultural landscape and a growing economy. Here’s a comprehensive summary:
History
- Ancient Kingdoms: Once home to powerful kingdoms, most notably Dahomey (1600s–1900s).
- Slave Trade: A key point in the transatlantic slave trade.
- French Colonization: Became part of French West Africa in the late 19th century.
- Independence in 1960: Gained independence from France as Dahomey.
- Recent History: Renamed Benin in 1975, with a transition to democracy in 1990.
Geography
- Location: In West Africa, bordered by Togo, Nigeria, Burkina Faso, and Niger.
- Land Area: Approximately 114,763 square kilometers.
- Terrain: Features a short coastline, lagoons, flat plains, and northern savannas.
- Climate: Tropical in the south, semi-arid in the north.
Economy
- Agriculture: Primary sector with products like cotton, palm oil, and cassava.
- Growth Areas: Tourism, textiles, and food processing industries are developing.
- Challenges: Economic development is hindered by corruption and underinvestment.
Neighboring Countries
- Nigeria: East
- Togo: West
- Burkina Faso: Northwest
- Niger: Northeast
Culture
- Languages: French (official), with indigenous languages like Fon and Yoruba.
- Religion: A blend of Christianity, Islam, and traditional Vodun (Voodoo) practices.
- Festivals: Vibrant cultural festivals, including the Voodoo Festival.
- Music and Art: Known for traditional music, dance, and colorful textiles.
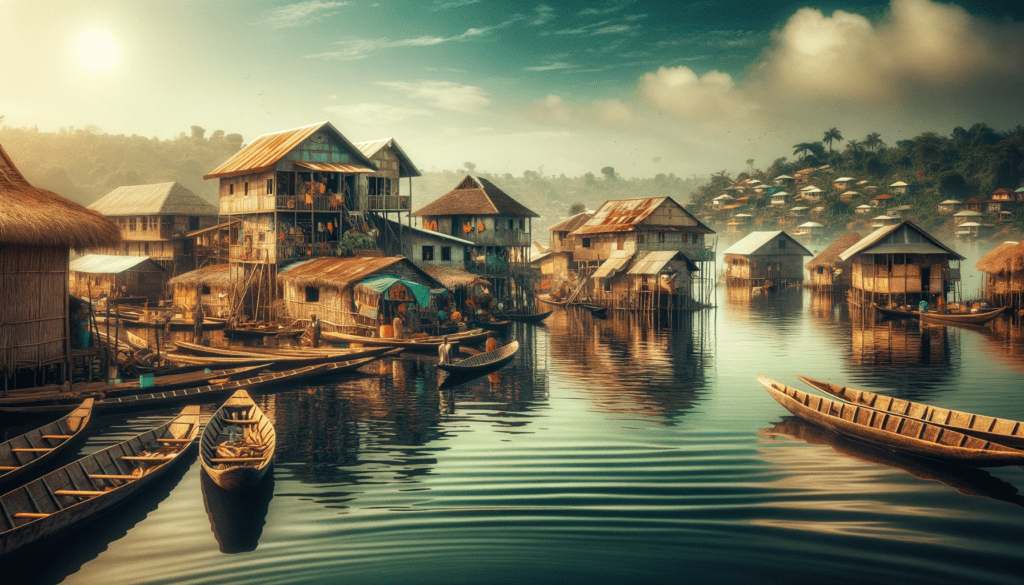
Tourism and Natural Beauty
- Historical Sites: Includes Ouidah, a center of the slave trade, and Abomey, the Dahomey Kingdom’s capital.
- Wildlife Parks: Pendjari National Park, known for its wildlife including elephants and lions.
- Cultural Significance: Rich in traditional crafts, architecture, and historical artifacts.
- Ganvie – Lake village lying in Lake Nokoué, near Cotonou.
Challenges
- Political Stability: Has maintained relative political stability in a turbulent region.
- Social Issues: Efforts are ongoing to improve education, healthcare, and women’s rights.
Conclusion
Benin’s rich historical legacy and cultural diversity, combined with its natural beauty and wildlife, make it an intriguing and culturally rich destination in Africa.

