Venezuela, located in the northern part of South America, is a nation that boasts diverse landscapes, a rich cultural heritage, and complex political and economic challenges. With a population of approximately 30 million people, Venezuela is a country of contrasts that offers a wide range of natural beauty and cultural experiences.
List of National and Public Holidays in Venezuela for the year 2024
- New Year’s Day – January 1, Monday, 2024
- Carnival – February 12, Monday, 2024
- Carnival – February 13, Tuesday, 2024
- Maundy Thursday – March 28, Thursday, 2024
- Good Friday – March 29, Friday, 2024
- Declaration of Independence – April 19, Friday, 2024
- Labour Day – May 1, Wednesday, 2024
- Battle of Carabobo – June 24, Monday, 2024
- Independence Day – July 5, Friday, 2024
- Simon Bolivar’s Day – July 24, Wednesday, 2024
- Indigenous Resistance Day – October 12, Saturday, 2024
- Christmas Eve – December 24, Tuesday, 2024
- Christmas Day – December 25, Wednesday, 2024
- New Year’s Eve – December 31, Tuesday, 2024
Country Profile: Venezuela

Geography:
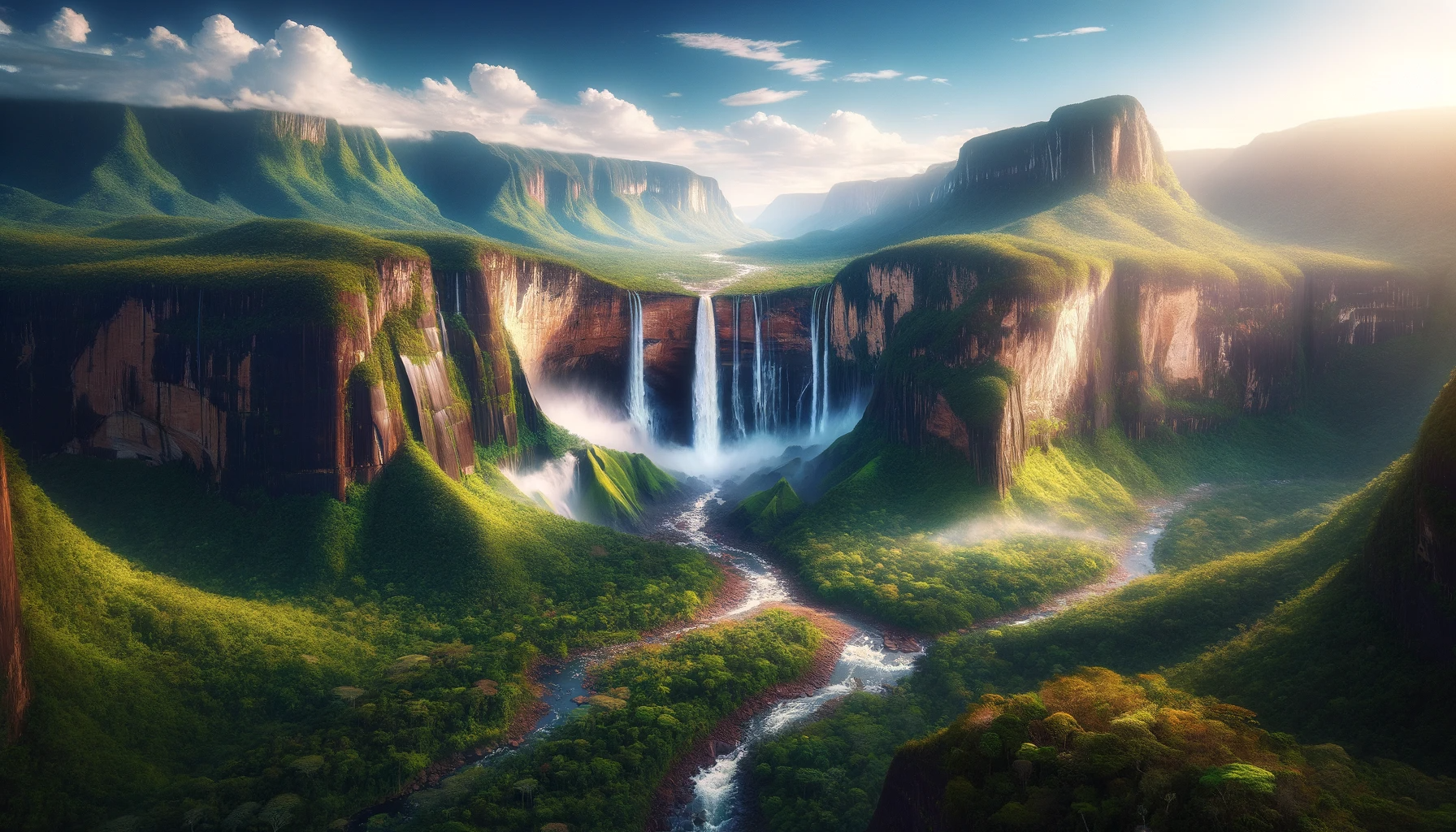
Venezuela’s geography is characterized by striking diversity. It boasts lush tropical rainforests, expansive plains, the Andes Mountains, and a long coastline along the Caribbean Sea. The country is home to the world’s highest uninterrupted waterfall, Angel Falls, located in Canaima National Park.
Venezuela shares its borders with several neighboring countries in South America. Its neighboring countries are:
Venezuela’s northern coastline is along the Caribbean Sea, which forms its northern border. These neighboring countries play important roles in trade, diplomacy, and regional relationships with Venezuela.
Capital and Major Cities:
The capital city of Venezuela is Caracas, a bustling metropolis situated in the northern part of the country. Other major cities in Venezuela include Maracaibo, Valencia, and Barquisimeto.
Culture:
Venezuela is a melting pot of cultures, shaped by indigenous, Spanish, African, and Caribbean influences. The majority of the population is mestizo (of mixed indigenous and European descent), followed by Afro-Venezuelans, Europeans, and indigenous peoples. Venezuelan culture is known for its music, including the lively rhythms of salsa and merengue, as well as its colorful festivals and traditional cuisine.
Economy:
Venezuela’s economy has historically relied heavily on oil production, with the country possessing some of the world’s largest oil reserves. However, economic challenges, including mismanagement and fluctuating oil prices, have led to significant economic instability in recent years. This has resulted in hyperinflation, shortages of basic goods, and a decline in living standards. Agriculture, manufacturing, and services also play a role in the economy.
Language:
Spanish is the official language of Venezuela, and it is widely spoken throughout the country. Indigenous languages are spoken in some remote areas, particularly in the Amazon rainforest.

Tourism in Venezuela:
Venezuela has immense potential for tourism, with its natural beauty, including the Canaima National Park and Angel Falls, the Orinoco Delta, and the stunning Caribbean coastline. The country offers opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, bird watching, and wildlife exploration. However, due to political and economic challenges, tourism has declined in recent years, and safety concerns have arisen in some areas.
Challenges:
Venezuela faces numerous challenges, including political instability, economic crisis, and social unrest. The country has experienced political polarization and protests, leading to changes in leadership. The economic crisis has resulted in severe shortages of basic necessities, a collapsing healthcare system, and emigration of a significant portion of the population. These challenges have led to a humanitarian crisis that continues to impact the daily lives of Venezuelans.
Conclusion:
Venezuela is a country of immense natural beauty and cultural diversity, but it faces significant political and economic challenges that have affected the well-being of its citizens and the potential for tourism. While the country’s landscapes and culture remain compelling, ongoing instability and safety concerns have impacted its ability to attract travelers. As Venezuela navigates its complex political and economic landscape, it remains a place of intrigue and potential for those interested in its diverse heritage and breathtaking natural wonders.

